Electrostatic force
Coulomb’s Law
F = kq1q2/r2
where k=1/4πεo=9×109Nm2C-2
εo = 8.85×10-12C2m-2N-1
See a solved example at Buzztutor.comVector notation
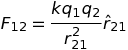
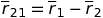
Electrostatic field
Electric field due to a point charge
E = F/qo = kq/r2 N/C
See a solved example at Buzztutor.comE due to circular loop of charge (radius r) at a distance x from the center
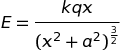
Electric dipole
Dipole moment
 Cm
Cm
Electric field at an axial point of a dipole
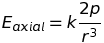
Electric field at an equatorial point of a dipole

Torque acting on a dipole in a uniform electric field
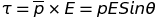
Potential energy of a dipole in a uniform electric field
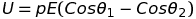
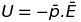
Electrostatic potential
Electrostatic potential difference
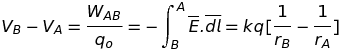
Potential due to a point charge
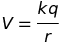
Potential at an axial point of a dipole
 if
if  then
then 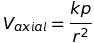
Potential at an equatorial point of a dipole
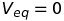
Relation between electrostatic field and potential gradient
Electric field = negative of the potential gradient
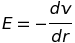
Electrostatic potential energy
Electrostatic potential energy of two point charges
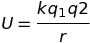
Gauss’ theorem
Electric flux
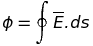
Gauss’ theorem
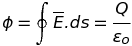
Definition: Electric flux ϕ through any closed surface is 1/εo times the net charge Q enclosed by the surface.
Electric field E due to infinitely long straight wire (a line charge)
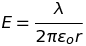
Electric field E due to thin infinite plane sheet of charge
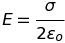
Electric field between two thin infinite plane parallel sheets of charge
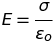
Electric field due to uniformly charged spherical shell
 for r > R
for r > R
 for r < R
for r < R
 for r = R
for r = R
Capacitance
 Farad 1F = 1 C/V
Farad 1F = 1 C/V
Isolated spherical conductor
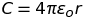
Parallel plate capacitor
 or
or  where
where
 and k is dielectric constant
and k is dielectric constant
Capacitors in series
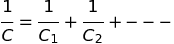
Capacitors in parallel
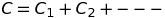
Energy stored in a capacitor
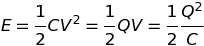
Energy density 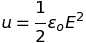
Common potential
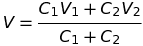
C with conducting slab between the two plates
 where t is thickness of slab [t < d]
where t is thickness of slab [t < d]
C with dielectric slab between the two plates
 where k is the dielectric constant
where k is the dielectric constant